Authors (3): Y. Zhu, C. Romain, C. K. Williams
Themes: Transformations DOI: 10.1038/nature21001
Citations: 2465
Pub type: article-journal
Pub year: 2016
Publisher: Springer Science and Business Media LLC
Issue: 7633
License: http://www.springer.com/tdm
Publication date(s): 2016/12 (print) 2016/12/14 (online)
Pages: 354-362
Volume: 540 Issue: 7633
Journal: Nature
Link: http://www.nature.com/articles/nature21001.pdf
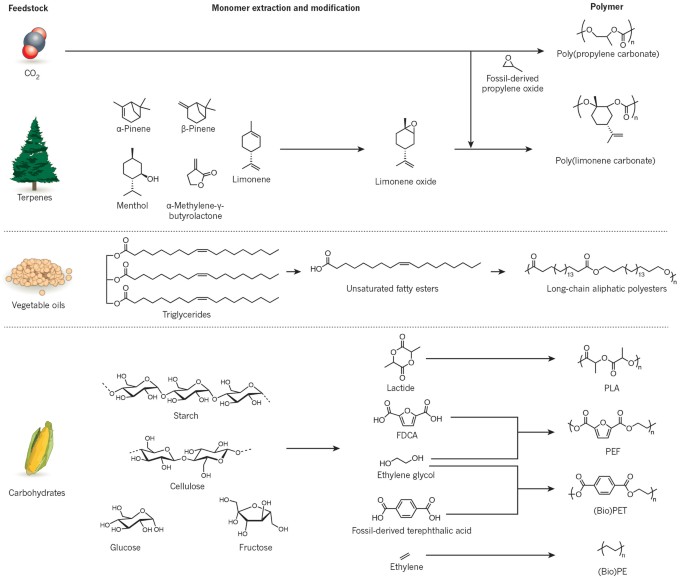
URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature21001Renewable resources are used increasingly in the production of polymers. In particular, monomers such as carbon dioxide, terpenes, vegetable oils and carbohydrates can be used as feedstocks for the manufacture of a variety of sustainable materials and products, including elastomers, plastics, hydrogels, flexible electronics, resins, engineering polymers and composites. Efficient catalysis is required to produce monomers, to facilitate selective polymerizations and to enable recycling or upcycling of waste materials. There are opportunities to use such sustainable polymers in both high-value areas and in basic applications such as packaging. Life-cycle assessment can be used to quantify the environmental benefits of sustainable polymers.
There are no objects associated to this publication
<< Previous Back Next >>